Turning Point Definition Math

Turning point definition a point at which a decisive change takes place.
Turning point definition math. Turning point synonyms turning point pronunciation turning point translation english dictionary definition of turning point. You turn change directions at a turning point so the name is appropriate. Mathematics maths a stationary point at which the first derivative of a function changes sign so that typically. Meaning pronunciation translations and examples.
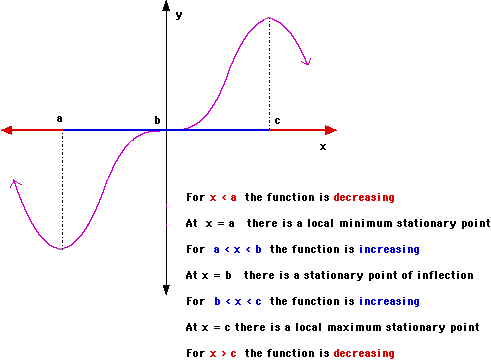
The point at which a very significant change occurs. However not all stationary points are turning points. Definition turning points of polynomials. If the function is differentiable then a turning point is a stationary point.
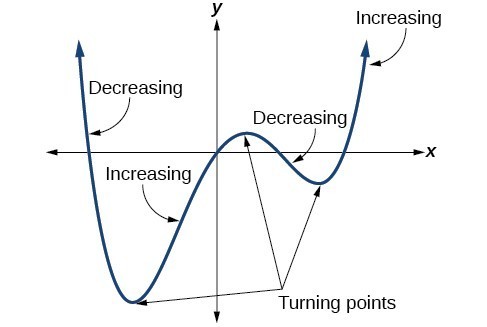
There are degree 1 or less. A turning point is either a local maximum point or a local minimum point. A turning point is a time at which an important change takes place which affects the. A hyperbola is two curves that are like infinite bows.
Turning point test jump to. The curve is either increasing or decreasing on both sides of this point. Also known as a stationary point. Any point p is closer to f than to g by some constant amount.
Notes about turning points. Use the term with the largest exponent introduction to algebra algebra basic definitions algebra index. Turning point a point on the graph at which the slope of the tangent changes its sign. The curve does not turn and hence it is not a turning point and the curve is stationary at this point.
Turning point definition is a point at which a significant change occurs. Thus a turning point of a polynomial always occurs at a horizontal tangent line. How to use turning point in a sentence. A point of horizontal inflection occurs in a monotonic increasing or monotonic decreasing curve.
A turning point is a point at which the derivative changes sign. Navigation search in statistical hypothesis testing a turning point test is a statistical test of the independence of a series of random variables. A turning point of a polynomial is a point where there is a local max or a local min. In other words the distance from p to f is always less than the distance p to g by some constant amount.