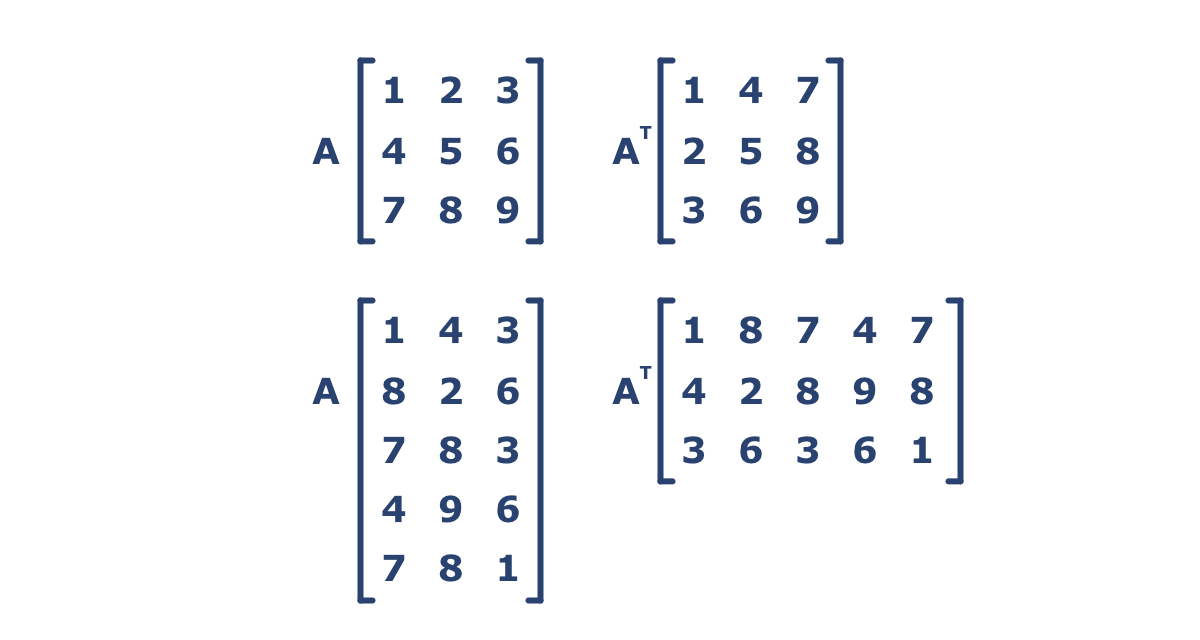
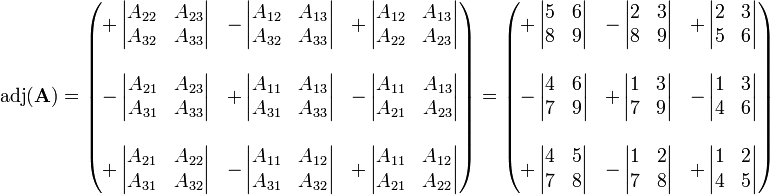Transpose Of A 3x3 Matrix Example

The algorithm of matrix transpose is pretty simple.
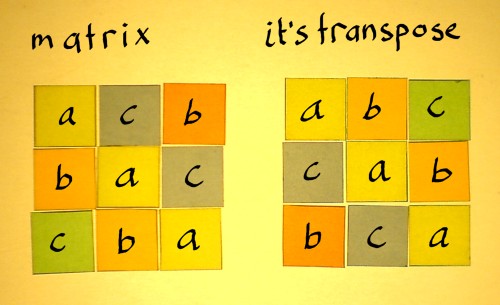
Transpose of a 3x3 matrix example. To transpose a matrix start by turning the first row of the matrix into the first column of its transpose. A new matrix is obtained the following way. Consider the following example problem approach. If a a ij be an m n matrix then the matrix obtained by interchanging the rows and columns of a would be the transpose of a.
If we take transpose of transpose matrix the matrix obtained is equal to the original matrix. Next transpose the matrix by rewriting the first row as the first column the middle row as the middle column and the third row as the third column. If the determinant is 0 the matrix has no inverse. Properties of transpose of a matrix.
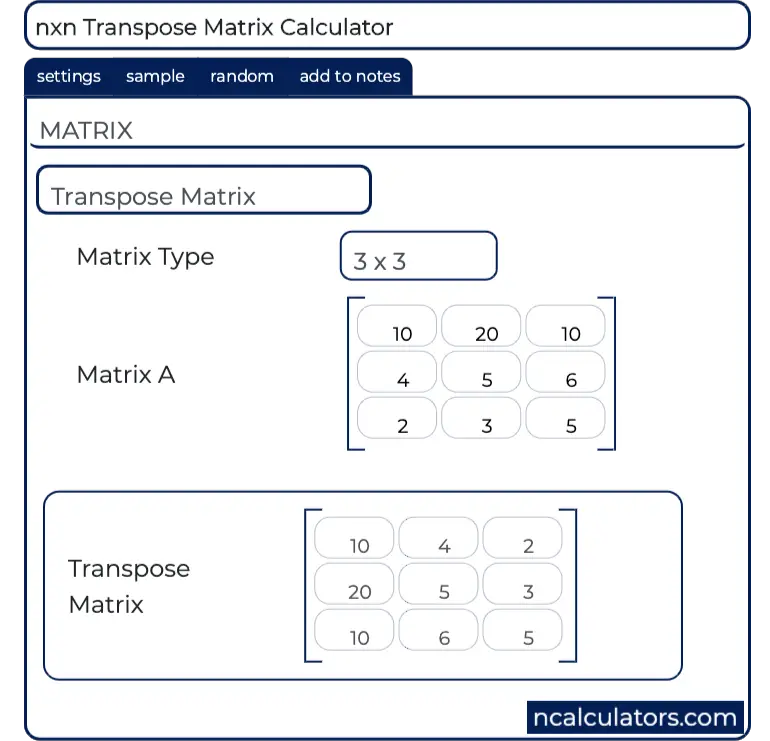
Initialize a 2d array to work as matrix. The transpose of a matrix is defined as a matrix formed my interchanging all rows with their corresponding column and vice versa of previous matrix. Store values in it. Of it is denoted by a or a t in other words if a a ij mxn thena a ji nxm for example.
Each i j element of the new matrix gets the value of the j i element of the original one. I transpose of the transpose matrix. Some properties of transpose of a matrix are given below. The transpose of a matrix is a matrix whose rows and columns are reversed the inverse of a matrix is a matrix such that and equal the identity matrix if the inverse exists the matrix is said to be nonsingularthe trace of a matrix is the sum of the entries on the main diagonal upper left to lower right the determinant is computed from all the.
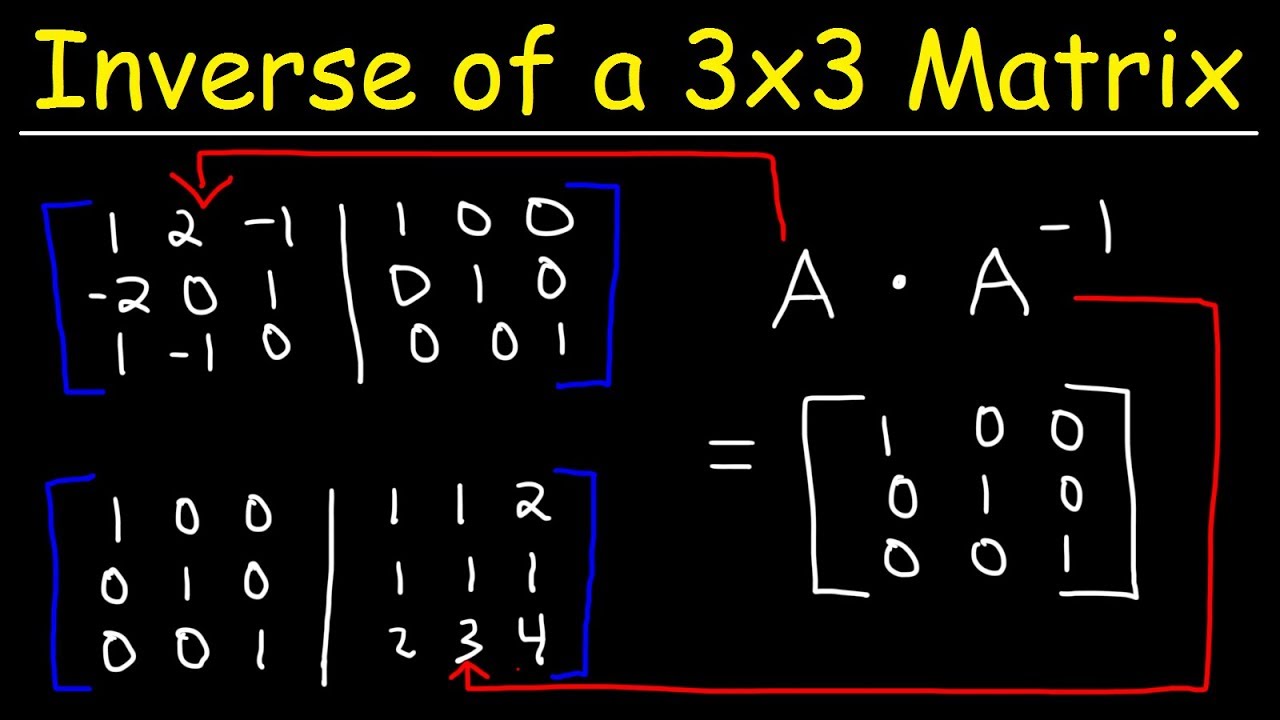
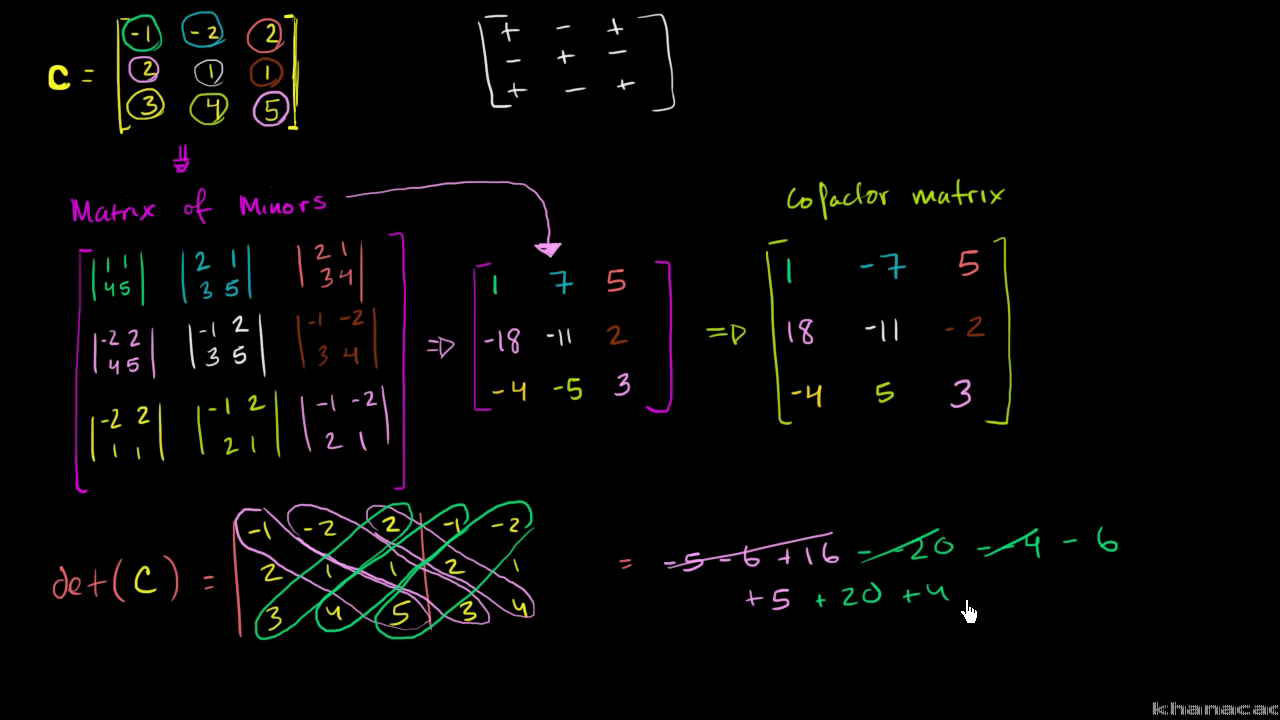
By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Dimension also changes to the opposite. Repeat this step for the remaining rows so the second row of the original matrix becomes the second column of its transpose and so on. To find the inverse of a 3x3 matrix first calculate the determinant of the matrix.
For example if you transpose a n x m size matrix you ll get a new one of m x n dimension. Find the transpose of that matrix. The new matrix obtained by interchanging the rows and columns of the original matrix is called as the transpose of the matrix.