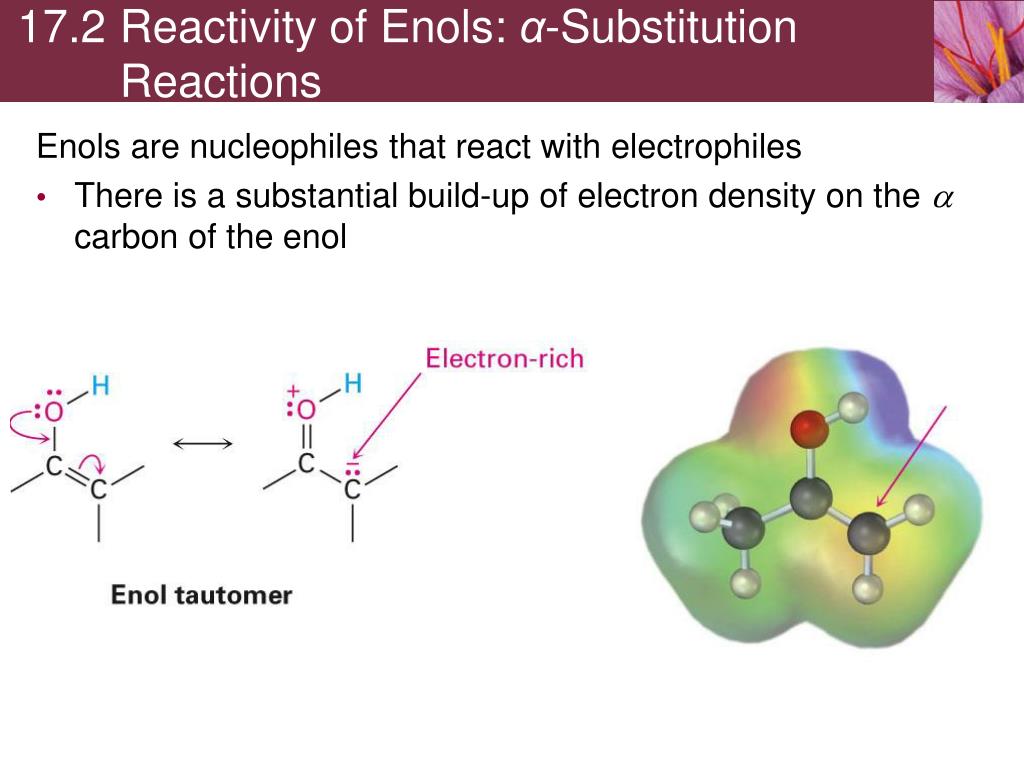
Substitution At Allylic And Vinylic Carbons

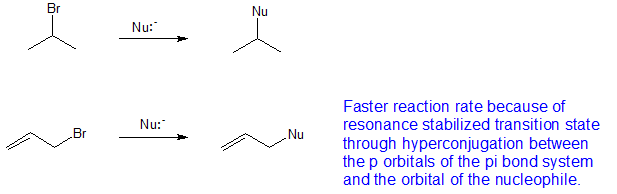
An allylic carbon is an sp3 carbon that is adjacent to a vinylic carbon.
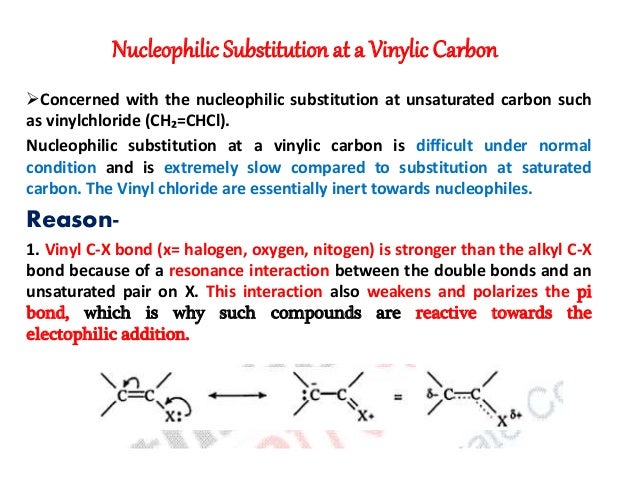
Substitution at allylic and vinylic carbons. S n 2 substitution. Inversion versus retention of configuration for nucleophilic substitution at vinylic carbon. It consists of methylene bridge ch 2 in between the vinyl group ch ch 2 and the rest of the molecule. This type of process is called an s n 1 substitution.
Bifunctional vinylboroate allylic acetate esters react with grignard reagents to form tertiary allylic boronates via an ate mediated allylic substitution amas approach. Nucleophilic substitution at an allylic aliphatic trigonal and sni reactions and nucleophilic substitution at a vinylic carbon reactivity effects of substrate content writer. Alternatively it is possible for nucleophile to attack directly at the allylic position displacing the leaving group in a single step in a process referred to as s n 2 substitution. Journal of the american chemical society 2001 123 24 5787 5793.
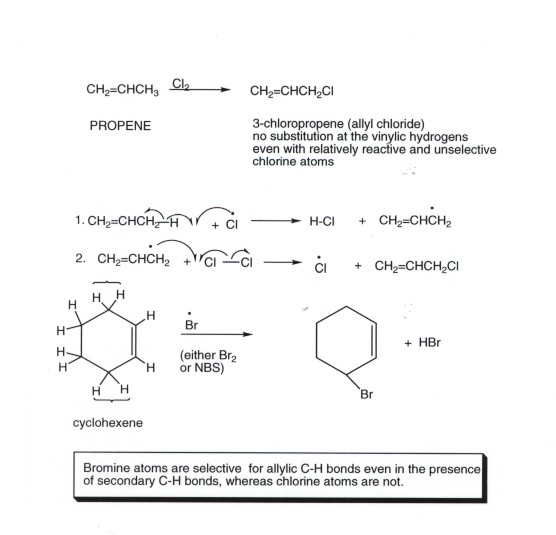
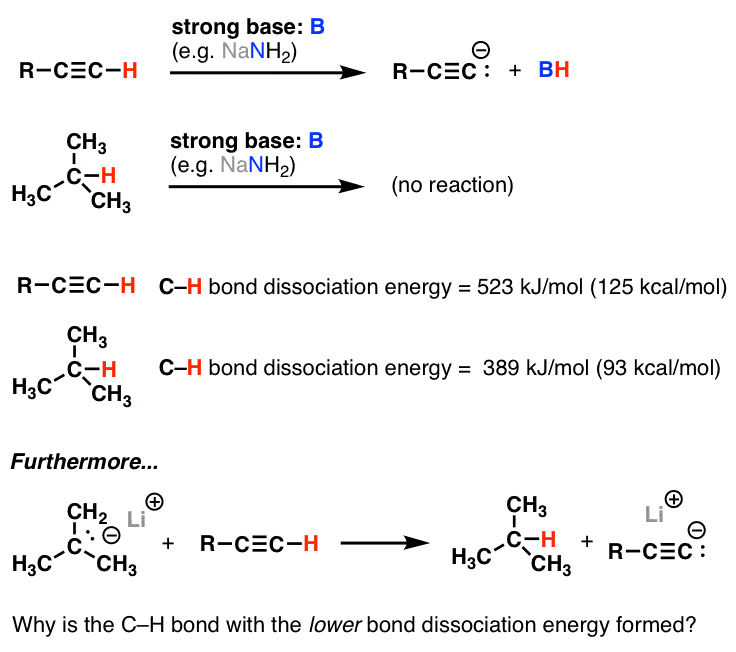
Allyl indicates a functional group with structural formula h 2 c ch ch 2 r where r is the rest of the molecule. The rate of substitution may be reduced by branching at the β carbons and this will increase elimination. Bases weaker than acetate pk a 4 8 give less elimination. As the table below shows the dissociation energy for the allylic c h bond is lower than the dissociation energies for the c h bonds at the vinylic and alkylic positions.
Mcquade synlett 2014 25 217 220. Atoms or groups attached to an allylic carbon are termed allylic substituents. N s o. Hence given that the halogen concentration is low substitution at the allylic position is favored over competing reactions.
This is likely in cases when the allyl compound is unhindered and a strong nucleophile is used. Boone and ann m. E2 elimination will dominate. This is because the radical formed when the allylic hydrogen is removed is resonance stabilized.
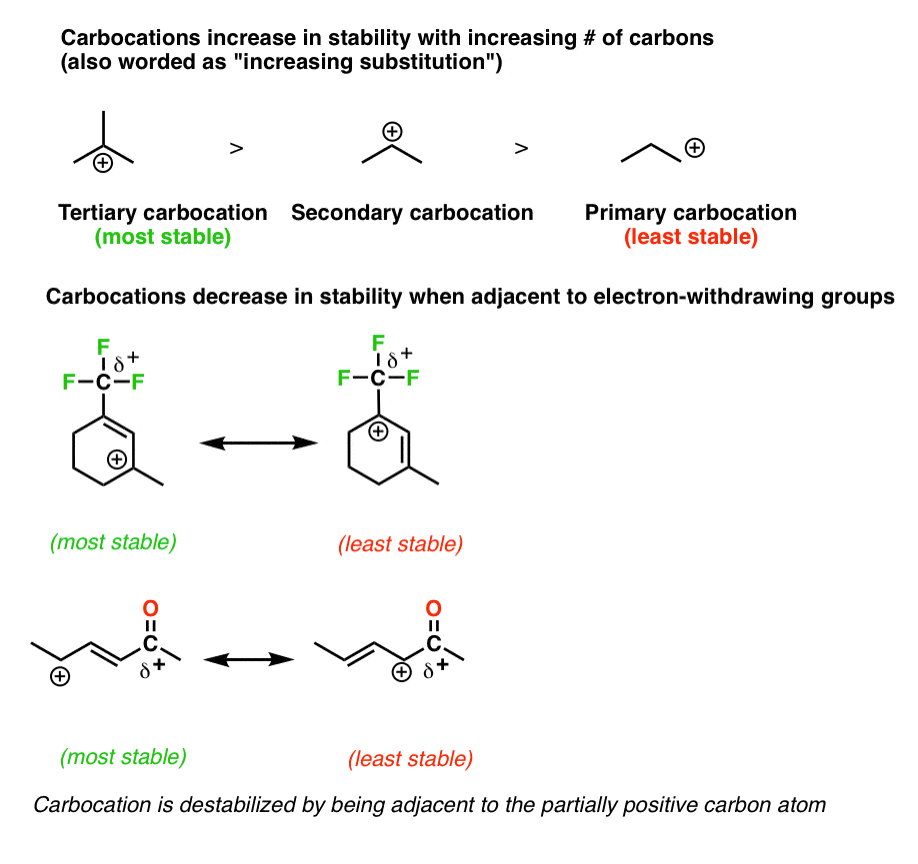
Therefore allyl group contains sp 2 hybridized vinyl carbon atoms and sp 3 hybridized allyl carbon atom. Key difference allylic vs vinylic carbons functional groups are very important in understanding the different physical and chemical properties of organic molecules the terms allylic and vinyl carbons indicate whether the carbon atom is bonded directly or indirectly to a double bond in a molecule. The method tolerates a wide range of substrates and grignard reagents. An allylic carbocation in which an allylic carbon bears the positive charge.